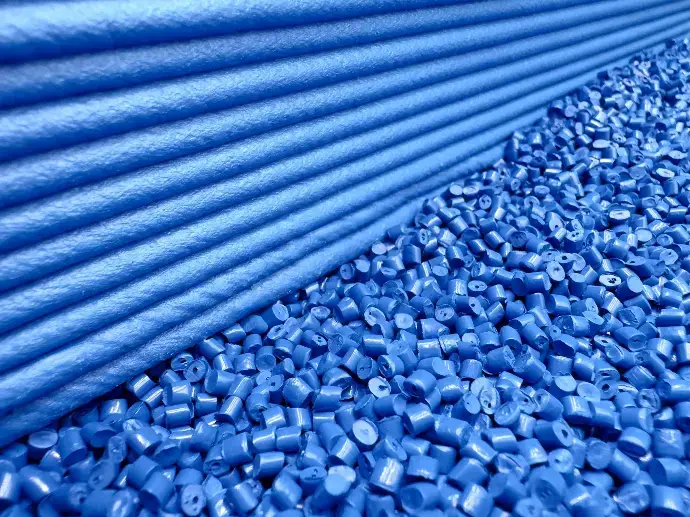
Innomerix has developed a new range of fibre reinforced materials. Using our newly commissioned compounding line we have the capability to add fibre reinforcement to our line of plastics. This give us the ability to create unique materials with high strength-to-weight ratios that can be used in the production of many unique products. These materials are suitable for injection moulding, additive-manufacturing, and a variety of other manufacturing techniques.
Fibre reinforced plastics are an excellent choice of material for manufacture as they combine the benefits of plastics, with mechanical properties that are comparable to metals. This can give high strength materials that are lightweight, while being corrosion resistant, non-conductive (both thermal and electrical) and non-magnetic. They are also able to be processed using techniques already common in the plastics industry, requiring no additional specialist equipment.
Tensile force/extension curve of PETG at different levels of glass reinforcement. As more glass is added, the material becomes more resistant to mechanical stress. High levels of glass lead to a stiff and strong compound.
We specialise in carbon fibre and glass fibre reinforcement in a wide range of commodity and engineering plastics. Our production facility and materials laboratory give Innomerix the ability to fine tune the properties of our materials to meet your needs.
Introducing fibres into thermoplastics is a different process to other fibre reinforced composites. Fibres are first treated with a wetting agent; this allows a bond to form between the polymer and fibre. Without this treatment, there is no interaction between polymer and fibre and the strength of the final material is limited. The fibres and polymer are then melt-mixed and extruded to create a homogeneous material. This material is cooled and cut into pellets before being bagged. These pellets are designed for ease of feeding for your manufacturing process.
Glass fibre reinforced plastic compounds are a low-cost alternative to metals. The increased tensile and flexural strength, improved heat deflection temperature can give some resins mechanical properties that are comparable to metals. There is an added cost saving as processing techniques are less expensive compared to making metal parts.
Higher levels of glass lead to a stiffer, stronger compound. Carbon fibre gives a much stronger product, even when compared to glass reinforced materials. Lower additions of carbon fibre are required to achieve higher strengths. Carbon fibre is also much lighter, giving a very high strength to weight ratio material.
Carbon fibre gives an even greater strength improvement than glass fibre. It also has a significantly lower density, giving parts that are extremely strong with very low weights. This material is often used in aeronautic applications, as the low weight also for more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Fibre reinforced materials offer a significant advantage in large format 3D printing. The incorporation of mechanically strong fibres helps combat shrinkage and warping – a major problem in printing large parts. While shrinkage rates can be small for certain materials, (0.1-1% depending on the resin used) over large print areas, the final amount of shrinkage can be significant. This leads to poor stacking and an inability to print certain sized parts. Innomerix glass and carbon fibre reinforced materials are stabilized against this, giving high quality printed parts.
If you need assistance with TDS and SDS materials, please don't hesitate to contact our skilled team for prompt and reliable support